Biogas
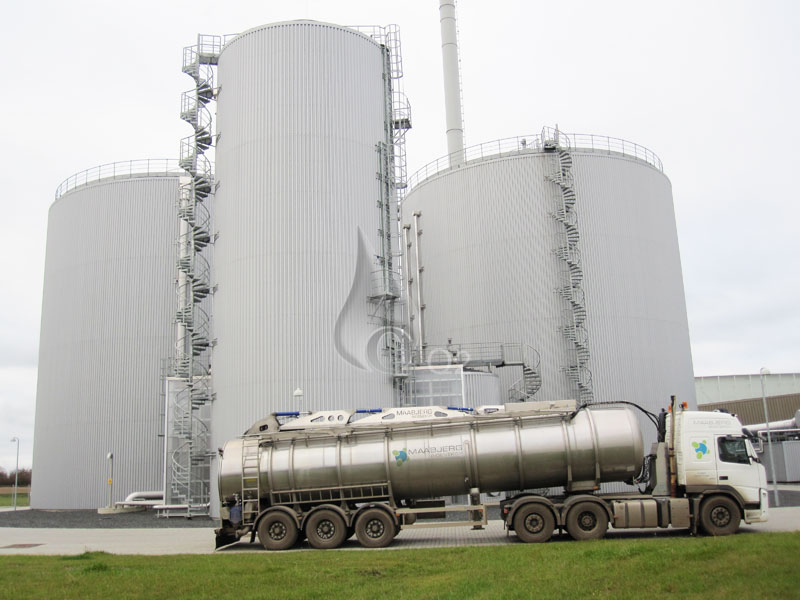

Biogas typically refers to gas produced by the anaerobic digestion or fermentation of organic matter, including manure, sewage sludge, biodegradable waste, wastewater, or any other biodegradable feedstock, under anaerobic conditions. Biogas is comprised primarily methane and carbon dioxide.
Treatment of biodegradable waste through anaerobic digestion with biogas production is a favoured way because valuable fuel can be produced while destroying disease-causing pathogens and reducing the volume as well as improving the quality of the disposed waste products.
Biogas produced from such treatment generally burns more cleanly than coal, and emits less carbon dioxide per unit of energy. The harvesting of biogas is an important part of environmental protection because methane is a potent greenhouse gas with a greater global warming potential of 21 times than carbon dioxide.
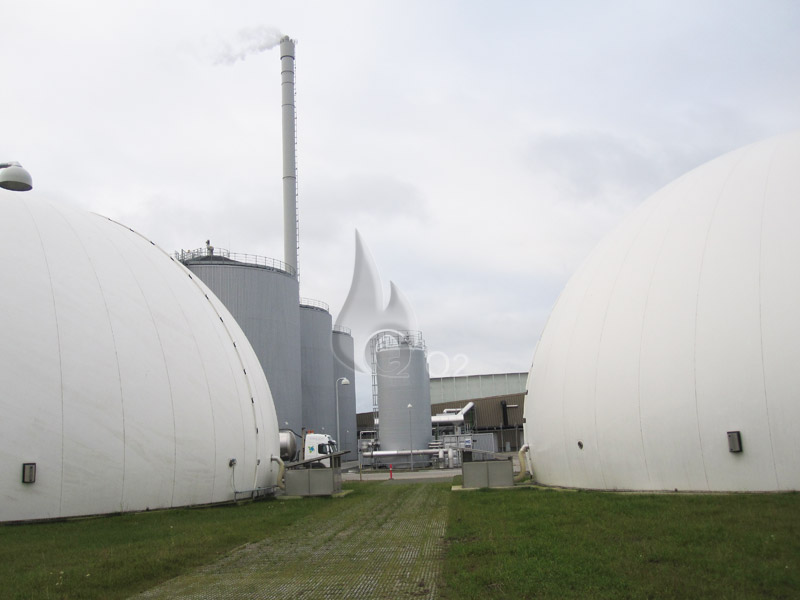

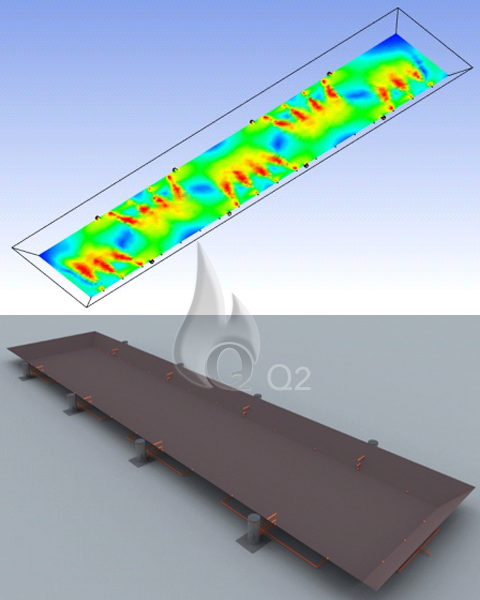
In a biogas plant, the degradation of different types of biomass is regulated and optimised in digesters. The biogas produced in these digesters are utilised to run gas engines which will then produce power and heat, or other applications, such as boilers, etc.
A good deal of biomass is traditionally stored in storage tanks or big lagoons from where methane releases to the atmosphere as a powerful greenhouse gas, being 21 times more destructive than CO2. A biogas plant achieves the benefit of both destructing the methane, and reducing the emission of greenhouse gas with the replaced electricity production. This process will also generate carbon credits which can then be sold and help to support the plant’s operation.
Q2 has a wide experience base within biogas utilisation. Q2 possesses the expertise to build biogas plants, from the initial feasibility studies through technical and economic calculations to actual
project implementation, including design, supply, construction, installation and commissioning, operation, and project management.